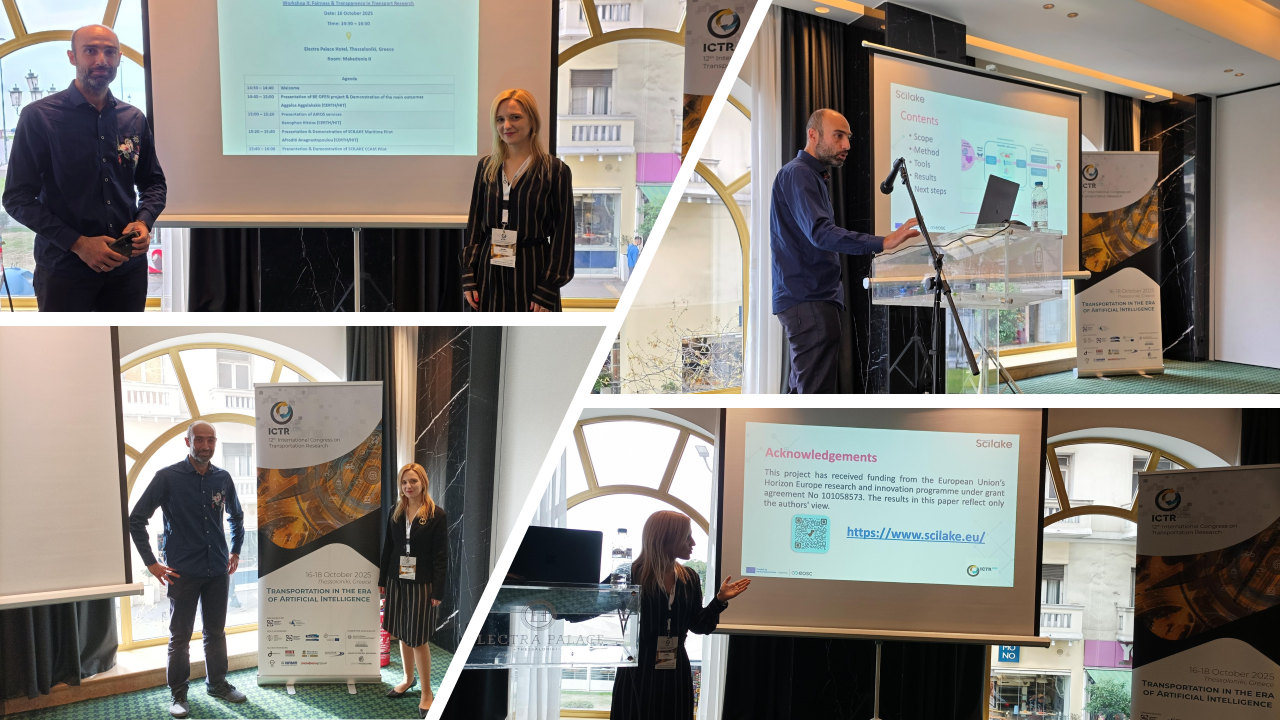
The SciLake project made a significant impact at the 12th International Congress on Transportation Research (ICTR 2025), held October 16–18, 2025, in Thessaloniki, Greece. Our partners from CERTH/HIT and ICCS organized a dedicated workshop and presented a conference paper highlighting how SciLake tools are advancing open science practices in transport research.
Workshop: Fairness & Transparency in Transport Research
On October 16, SciLake partners co-organized an engaging workshop titled "Fairness & Transparency in Transport Research." The event brought together 15 stakeholders from academia, industry and public authorities to explore how FAIR principles can transform transport research.
The workshop featured:
- Keynote presentations on Open Science and FAIR principles in transport research
- Live demonstrations of SciLake tools through the Maritime and CCAM (Cooperative Connected Automated Mobility) pilot cases, showcasing how Knowledge Graphs enable semantic connections between research data
- Interactive discussions where participants shared insights and recommendations for implementing FAIR principles
Afroditi Anagnostopoulou from CERTH/HIT presented the Maritime pilot, demonstrating how SciLake services, powered by Knowledge Graph infrastructure, enable researchers to access and share maritime transport data more effectively while maintaining semantic relationships. Athanasios Ballis from ICCS showcased the CCAM pilot, highlighting tools that promote transparency in autonomous vehicle research through graph-based data visualization.
Conference Paper: Open Science Insights from Maritime and CCAM Pilots
We also presented a research paper entitled "Open Science in Transport Research: Insights from the Maritime and CCAM Pilot Cases," co-authored by Afroditi Anagnostopoulou (CERTH/HIT), Athanasios Ballis (ICCS), Xenophon Kitsios (CERTH/HIT), Anastasia Bolovinou (ICCS), Vassilis Kappatos (CERTH/HIT), and Angelos Amditis (ICCS).
The paper demonstrates how FAIR data principles and Open Science practices can be implemented in transport research through two pilot cases. Central to this implementation is the use of semantic Knowledge Graphs that connect disparate data sources and enable researchers to discover relationships across datasets. The Maritime pilot addresses challenges of interoperability and data access, aiming to improve operational efficiency and situational awareness through digital platforms, open standards, and graph-based data structures. The CCAM pilot focuses on secure and equitable data sharing for automated transportation systems, promoting better collaboration between academia, industry, and public stakeholders through semantic knowledge representation.
Key findings from the paper include:
- Trust and transparency are operationalized through provenance tracking, citation context extraction, and graphical visualization of data links enabled by Knowledge Graph technologies
- Common challenges across both sectors include fragmented data ownership, limited interoperability, and institutional reluctance to share data
- SciLake's modular digital tools, including AvantGraph, Lake API, and SciNoBo, significantly mitigated these hurdles by offering explainable analyses, interoperable data access, and semantic Knowledge Graph capabilities that reveal hidden connections in research data
- Legal frameworks such as GDPR and EU data law play a crucial role alongside technical infrastructure in realizing FAIR principles
The paper's recommendations emphasize:
- Expanding standardization efforts to ensure consistency across transport sub-sectors, leveraging Knowledge Graphs to harmonize domain-specific semantics
- Involving broader stakeholder groups in co-designing data governance models
- Investing in infrastructure that supports transparency, interoperability, and reuse through semantic technologies
- Policy incentives to encourage private sector participation while ensuring data privacy and ethical compliance
Rather than presenting Open Science as a one-size-fits-all solution, the paper highlights the importance of domain-specific configurations of FAIR principles. Knowledge Graphs emerge as a critical enabler for capturing domain semantics while maintaining interoperability. The authors conclude that the shift towards more open, inclusive, and data-driven transport research is not only possible, but already underway when supported by aligned strategies, adaptive technologies, and semantic knowledge representation.
About ICTR 2025
ICTR 2025, co-organized by the Hellenic Institute of Transport (CERTH-HIT) and the Hellenic Institute of Transportation Engineers (HITE), focused on "Transportation in the Era of Artificial Intelligence." The conference has been a cornerstone of transportation research for 23 years, bringing together local and international communities to bridge research findings with policymaking efforts.
The event explored how AI is transforming transportation through advancements in autonomous vehicles, smart infrastructure, sustainability, and supply chain optimization: themes that align closely with SciLake's mission to make research data more accessible and actionable through Knowledge Graph technologies.
Impact and Next Steps
Feedback from participants emphasized the need for improved data accessibility and transparency in an increasingly digitalized transport sector. The results will be documented in SciLake deliverables, with follow-up activities including working with stakeholders to promote implementation of FAIR and Open Science principles through semantic Knowledge Graph infrastructure.
All materials (agenda and presentations) from the workshop are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17481960.
The conference paper is also available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17481746.
For more information about SciLake Pilots visit https://scilake.eu/case-studies